The earlier you can diagnose vision problems, the faster your child can benefit from the appropriate intervention. If the eyes of the baby have an opacity, or you see them not gazing in the correct direction when you play a sound, You should take them to an optometrist or an Opthalmologist to get them checked for any visual abnormalities.
Measurement of visual acuity using an eye chart is recommended in children starting at 2.5 yrs years of age. Some vision problems, such as lazy eye, are best treated if they are detected and corrected as early as possible while the child’s vision system is still developing.
What is a pediatric optometrist?
A pediatric optometrist is an eye doctor (a Doctor of Optometry) who specializes in children’s eye health.
Eye test of children is difficult because of their apprehension and brief attention spans
Pediatric optometrist have additional training, education and experience working with children, performing kid-friendly eye exams and testing, and recognising and treating child-specific eye conditions.
In most children less than 2.5 years of age, preverbal methods must be used Clinical methods for infants involve an estimate of fixation and following behavior

When should a child be referred to a pediatric ophthalmologist?
The pediatric eye exam needs Patience. Unlike adult patients, children often are
not able to realize or communicate what is wrong with their eyes. Moreover, they often are not willing participants in the examination and so it requires significant effort to gain all
the necessary information. To obtain a good history, we have to ask the right questions to both the parent and child, as well as direct our line of questioning so that the least amount
of time is wasted while we have the child’s interest. Children must be engaged throughout the visit and the physician must hold their attention and learn how to “play” with them during the exam.
Do I need an Eye Doctor for my child?
If Children have symptoms of blurred vision, inability to read, sitting too close to the television, squinting, or poor performance in school, do take them to an Eye Doctor. If the child has been referred by a primary care provider or have failed school screening examination, you need to take your child to an eye doctor.
In addition to subnormal vision, children may complain of ocular fatigue, inability to study, letter reversal while reading and writing, and reading difficulty.
Development of Vision in children
The period of visual maturation is the critical period during which the visual system is affected by external influences. Most of the maturation of the visual system is thought to occur during the first 3 years of life, although some plasticity remains between 3 and 8 years of age, or even longer to some degree. One author describes three critical periods in the development of visual acuity and amblyopia :
– The period of development of visual acuity (from birth
to 3 to 5 years of age)
– The period during which deprivation may cause amblyopia
(from birth to 7 or 8 years of age)
– The period during which recovery from amblyopia can
be achieved (from the time of deprivation to adolescence
or possibly young adulthood)
Test done by Pediatric optometrist
The most widely used test is preferential looking. Forced choice preferential looking (3), operant preferential looking and current variations of the acuity card procedure have
been developed to provide a simple, efficient method of assessing visual acuity in infants, young children, and nonverbal patients.
Test of Visual Acuity in the Older Child
After the age of 2.5 years, children will increasingly be able to read a chart to determine their visual acuity. These tests measure recognition acuity: the ability to differentiate one
stimulus from a group of similar stimuli.

Paediatric eye exam for infants
Babies should be able to see as well as adults in terms of focusing ability, color vision and depth perception by 6 months of age.
Test done for paediatric eye exam for Babies
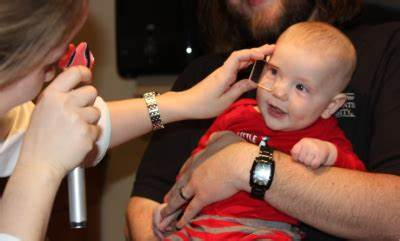
1. Pupil test
Tests of pupil responses evaluate whether the eye’s pupil opens and closes properly in the presence or absence of light.
2. Fixate and Follow test
“Fixate and follow” testing determines whether your baby’s eyes are able to fixate on and follow an object such as a light as it moves. (Infants should be able to fixate on an object soon after birth and follow an object by the time they are 3 months old.)
3. Preferential looking test
Preferential looking involves using cards that are blank on one side with stripes on the other side to attract the gaze of an infant to the stripes. In this way, vision capabilities can be assessed without the use of a typical eye chart.
Paediatric eye exam for Pre school children
1. LEA symbols
LEA symbols for young children are similar to regular eye tests using charts with letters, except that special symbols in these tests include an apple, house, square and circle.
2. Retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is a test that involves shining a light into the eye to observe the reflection from the back of the eye (retina). This test helps determine if your child has any clouding of the lens of the eye (congenital cataract) or significant refractive error.
3. Random dot stereopsis test
Random dot stereopsis testing uses special patterns of dots and 3-D glasses to measure how well your child’s eyes work together as a team.
4. Cover, Cover-Uncover, and Alternate Cover Tests
In the cover test, the child’s attention is attracted to a target. The vision of one eye is then occluded. The tested (uncovered) eye is observed for movement from a deviated position to one that fixes on the target (a sign of tropia, also called manifest strabismus). The untested eye is then uncovered and the tested eye is observed again for any drift out of alignment.
Cycloplegic refraction in Pediatric eye exam

A cycloplegic refraction is a procedure in which the eye doctor uses eye drops to relax the eye muscles in charge of focusing.
Cycloplegic eye drops causes pupils to dilate, and prevent you from over-focusing during your eye exam.Your eye doctor will have a wider view of the inside of your eyes, making it easier to detect signs of eye disease, such as glaucoma and macular degeneration.
Your eye doctor will also be able to more easily determine the full extent of your vision, without the concern that results may be skewed by inadvertent over-focusing.
Above mentioned Cycloplegic eye drops may be prescribed by the doctor and you may be asked to visit again in a few days.
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.