Pediatric Eye test Guide
What is a pediatric eye & vision examination?
The pediatric optometrist and Pediatric Optometry
A Pediatryc eye examination includes-
- Case History: The eye care professional will gather information about the child’s medical history, family history of eye conditions, and any specific concerns related to vision or eye health.
- Visual Acuity Testing: This involves assessing the child’s ability to see clearly at different distances using an eye chart. Depending on the child’s age and developmental level, different techniques may be used to measure visual acuity.
- Refraction: Refraction determines if a child needs corrective lenses (glasses) to improve their vision. The eye care professional uses a phoropter or other instruments to determine the appropriate prescription.
- Binocular Vision and Alignment: This assesses how well the child’s eyes work together and if they are properly aligned. Problems with eye coordination can lead to conditions like strabismus (crossed or misaligned eyes).
- Eye Health Evaluation: The eye care professional examines the internal and external structures of the eyes using specialized equipment. This helps detect any signs of eye diseases, abnormalities, or conditions such as amblyopia (lazy eye).
- Pupil Examination: The size and responsiveness of the pupils are checked. Changes in pupil size or reactions can indicate underlying issues.
- Color Vision Testing: For older children, color vision testing may be conducted to identify any color vision deficiencies.
- Dilation: In some cases, the eye care professional might choose to dilate the child’s pupils using eye drops to get a better view of the internal eye structures. This allows for a more thorough assessment of eye health.
- Recommendations and Treatment: Based on the examination findings, the eye care professional will recommend any necessary treatments, interventions, or follow-up appointments. This could include prescribing glasses, recommending vision therapy, or suggesting further medical evaluations if any concerns are detected.
How is Pediatric eye exam done?
Measurement of visual acuity using an eye chart is recommended in children starting at 2.5 yrs years of age. Some vision problems, such as lazy eye, are best treated if they are detected and corrected as early as possible while the child’s vision system is still developing.
Development of Vision in children

The period of visual maturation is the critical period during which the visual system is affected by external influences. Most of the maturation of the visual system is thought to occur during the first 3 years of life, although some plasticity remains between 3 and 8 years of age, or even longer to some degree. One author describes three critical periods in the development of visual acuity and amblyopia :
– The period of development of visual acuity (from birth to 3 to 5 years of age)
– The period during which deprivation may cause amblyopia (from birth to 7 or 8 years of age)
– The period during which recovery from amblyopia can be achieved (from the time of deprivation to adolescence or possibly young adulthood)
We have written detailed article on this topic.
Paediatric eye exam/pediatric eye exam – Eye test for babies and kids
Pediatric Eye test Guide Printable
This Pediatric Eye test Guide Printable guide tells you :
This guide provides information on several topics related to pediatric eye care:
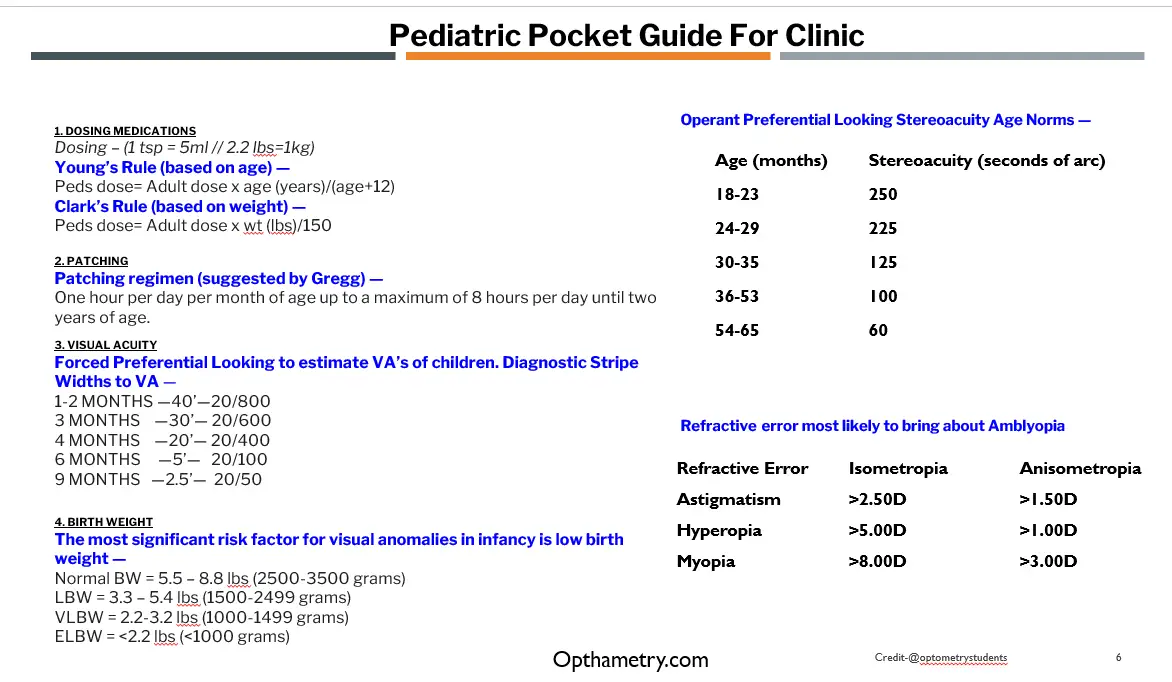
- Dosing Medications:
- It explains how to calculate medication doses for pediatric patients.
- Two rules are mentioned: Young’s Rule based on age and Clark’s Rule based on weight.
- Patching:
- It outlines a recommended patching regimen for treating certain eye conditions in children.
- The regimen involves wearing an eye patch for a specific duration based on the child’s age.
- Visual Acuity:
- It presents methods for estimating visual acuity (VA) in children using Forced Preferential Looking.
- Diagnostic Stripe Widths corresponding to different ages and their estimated VA are provided.
- Operant Preferential Looking Stereoacuity Age Norms are listed, indicating typical stereoacuity levels for different age ranges.
- Amblyogenic Refractive Error:
- It discusses refractive errors that are most likely to lead to Amblyopia (lazy eye).
- Specific refractive error thresholds are given for isometropia, anisometropia, astigmatism, hyperopia, and myopia.
- Birth Weight:
- It emphasizes the significance of birth weight as a risk factor for visual anomalies in infancy.
- Different weight categories are defined: normal birth weight, low birth weight (LBW), very low birth weight (VLBW), and extremely low birth weight (ELBW).

Reference to above chart taken from Optometrystudents.com
Follow us in Facebook for daily Eye care articles