Astigmatism is a common refractive error that affects the way light enters the eye, causing blurred or distorted vision. Among the various types of astigmatism, mixed astigmatism stands out as a unique and complex condition.
What is Mixed Astigmatism?
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea or lens of the eye has an irregular shape, causing light to focus on multiple points instead of a single point.
Mixed Astigmatism definition:
Mixed astigmatism, also known as compound astigmatism, is a specific form of astigmatism where one meridian is nearsighted (myopic) and the other meridian is farsighted (hyperopic). Essentially, it combines elements of both myopic and hyperopic astigmatism within the same eye.
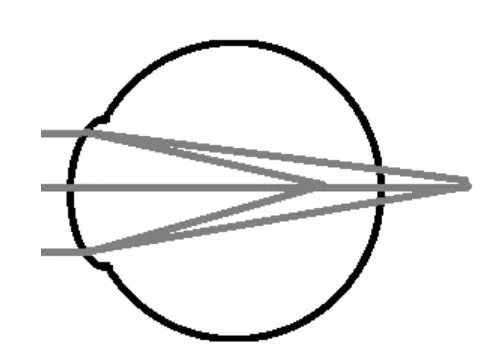
The principal meridans of the eye are opposites; one is myopic and the other is hyperopic.
Mixed Astigmatism Example:
- +1.0 -4.0 x 080 – In plus cylinder:
- -3.0 +4.0 x 170 -In Minus Cylinder
The spherical component is plus in minus-cylinder format but minus in plus-cylinder format, therefore, it indicates mixed Astigmatism.
Example 2:
- -5.0 +9.0 x 090- In minus cylinder:
- +4.0 -9.0 x 180- In plus cylinder
The spherical component is plus in minus-cylinder format but minus in plus-cylinder format, therefore, it indicates mixed Astigmatism.
Causes of Mixed Astigmatism:
- Corneal or Lenticular Irregularities: Mixed astigmatism can result from irregularities in the cornea or lens shape. Corneal irregularities are more common and can be present from birth or develop over time due to factors such as injury, surgery, or progressive changes in the eye.
- Genetic Factors: There may be a genetic predisposition to mixed astigmatism, as certain eye shapes can be inherited, increasing the likelihood of astigmatism in general.
Symptoms of Mixed Astigmatism:
- Blurred or Distorted Vision: The primary symptom is blurred vision, which can affect both near and distant objects.
- Eye Strain and Fatigue: Individuals with mixed astigmatism may experience eye strain and fatigue, particularly after prolonged periods of reading or using digital devices.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches, especially after visually demanding tasks, may be a symptom of mixed astigmatism.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: A comprehensive eye examination, including refraction testing, is essential for diagnosing mixed astigmatism. This examination helps determine the extent of the refractive errors in each meridian.
- Prescription Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses: Corrective lenses, either eyeglasses or contact lenses, are the most common and effective treatment for mixed astigmatism. These lenses are precisely crafted to counteract the myopic and hyperopic components of the condition.
- Refractive Surgery: In some cases, individuals may opt for refractive surgery, such as LASIK, to reshape the cornea and correct mixed astigmatism. However, surgery is typically considered when the prescription is stable and within certain parameters.
Mixed Astigmatism LASIK
Treatment of mixed astigmatism with laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) is complex as the correction requires flattening the cornea in one meridian while steepening the cornea in the other meridian. The bitoric technique has become the most popular approach and has been tested across a variety of platforms.
What are the other types of Astigmatism?
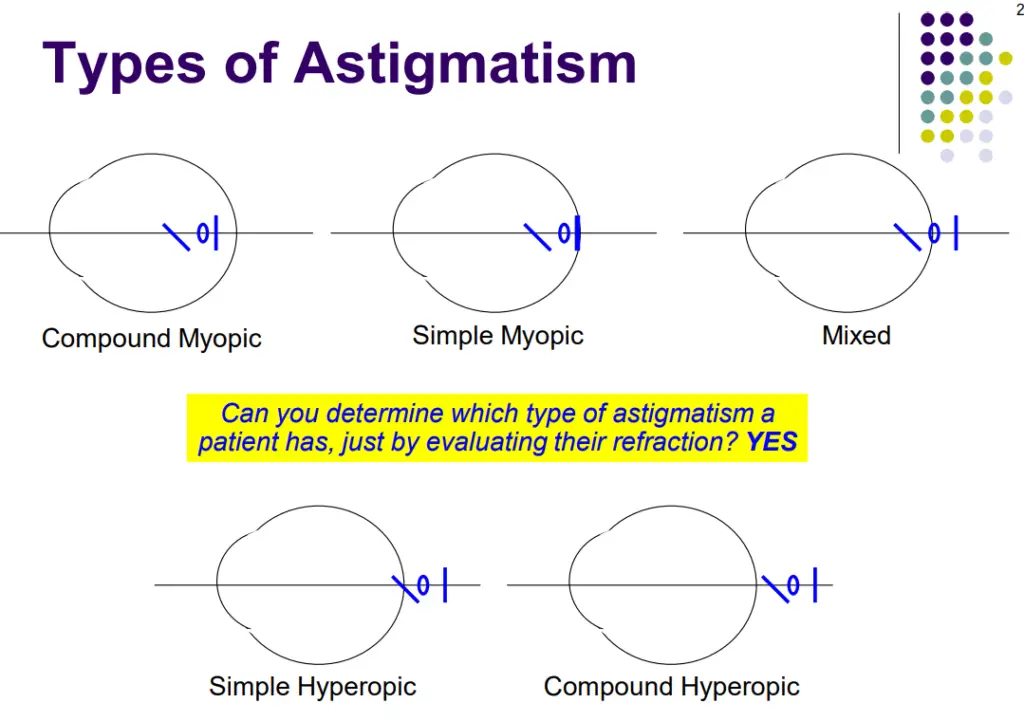
Credit- aao
With all types of astigmatism light rays come together to form not one but two focal points. The mere fact that there are two focal points formed, instead of just one (in the normal seeing eye) creates vision problems.
First Type
The first type of astigmatism is called Simple Myopic Astigmatism, where light comes to two focal points: one before the retina, and one on the retina.
Second Type
The second type is called Simple Hyperopic Astigmatism, where light comes to two focal points: one on the retina and another focus point that would be a virtual point behind the retina.
Third Type
The third type is called Compound Myopic Astigmatism where light comes to two focal points, both of which are before the retina but at two different locations before the retina.
Fourth Type
As you might have imagined, the fourth type is called Compound Hyperopic Astigmatism where light comes to focal points both of which would be in a virtual location behind the retina but at different virtual locations behind the retina.
Fifth Type
Finally, the fifth type is called Mixed Astigmatism where light rays come to two focal points, one of which is before the retina and the other of which is behind the retina
Follow us in Facebook
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.