Ophthalmic electrophysiology is a series of tests that measure how different parts of the eyes and vision system respond to light.Results may differentiate between maculopathies, retinopathies, and optic neuropathies. Accurate diagnosis requires incorporation of complementary clinical findings.
These tests check how the eyes and brain process what one is seeing by measuring the electrical activity in the retina and optic nerves.
When are Ophthalmic Electrophysiology test indicated
- Retinitis pigmentosa.
- Achromatopsia (a form of color blindness).
- Optic nerve disease.
- Before surgery
Who performs ophthalmic electrophysiology?
Trained technicians perform ophthalmic electrophysiology in a specially equipped lab
What are Ophthalmic Electrophysiology devices?
Ophthalmic Electrophysiology devices are-
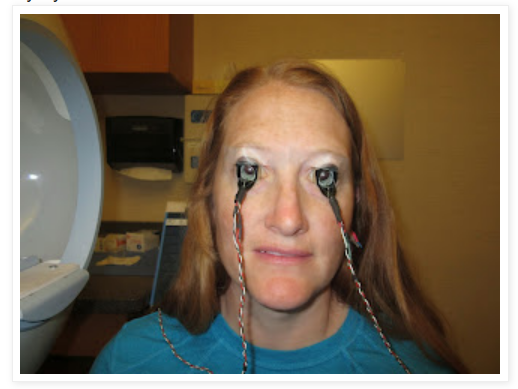
- Electroretinography (ERG): This test measures your retina’s response to light. In addition to the EEG leads, very thin wires will be placed over the front of your eye, directly above your bottom eyelid. The technician will flash bright lights in front of your eyes to measure your retina’s activity.
- Visual evoked potential (VEP): This test measures how your optic nerve responds to light. EEG leads will be placed on your scalp or face and you’ll look at patterns on a computer screen.
- Electro-oculography (EOG): This test measures the electrical potential across your retinal pigment epithelium, a single layer of cells that sits just behind your retina. The technician will place EEG leads on the inner and outside corners of your eyes. They’ll measure how well the pigmented epithelium cells in your retinas are functioning.
ERG eye
The ERG arises from currents generated directly by retinal neurons in combination with contributions from retinal glia. Importantly, the ERG is an objective measure of retinal function that can be recorded non-invasively under physiological conditions.
ERGs are often recorded using a thin fiber electrode that is placed in contact with the cornea or an electrode that is embedded within a corneal contact lens. These electrodes permit the electrical activity generated by the retina to be recorded at the corneal surface. The ERG can be elicited by diffuse flashes or patterned stimuli.
The International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV) has introduced standards for the different forms of ERG recordings. The ERG has important clinical utility, in that it provides diagnostic information concerning a variety of inherited and acquired retinal disorders. Moreover, the ERG can be used to monitor disease progression and evaluate retinal toxicity due to various drugs or retained intraocular foreign bodies.
Electro-oculography (EOG):
The clinical electro-oculogram (EOG) is an electrophysiological test of the outer retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in which changes in the electrical potential across the RPE are recorded. The test utilizes a single red light which alternates from left to right; first in a dark
adapted and then in light adapted conditions. Patients follow the light in smooth saccadic motions as electrodes on either side of the eyemeasure the voltage change. The Arden Ratio, which is the light peak-dark trough ratio, is calculated at the end of the test.
VEP
Visually Evoked Potentials (VEP) utilize occipital zone electrodes to record signals measured at the visual cortex to determine visual pathway integrity. VEPs that utilize flash or pattern stimuli may be used.
Pattern VEP
A pattern VEP presents a checker board pattern to central vision. The standard pattern reversal protocol is used for most patients; the pattern onset protocol is more effective for patients with nystagmus. Standard VEP protocols include 1- and 3-channel recordings as well as full and hemi field stimuli. The timing and amplitude of the PIOO biomarker is useful for investigating optic nerve disease and post-retinal visual pathway dysfunction.
Flash VEP
A flash VEP presents a series of flashes that stimulate the entire visual field. This test is primarily used as an assessment of visual pathway integrity in children and those with media opacities or ocular trauma.
Stepwise Sweep VEP
A method for objectively assessing visual acuity. Sweep VEP utilizes a black & white, low contrast checker board pattern onset method to stimulate a fixating patient. A Laplace transform and Fourier analysis is performed in automatically estimating visual acuity. Tests are
available for normal, low, and very low vision patients and can be useful for those with unexplained, psychogenic, or non-organic vision loss.
Apart from this there are-
Psychophysical Ophthalmic test
Psychophysical tests are a category of subjective tests which require patients to consciously respond to light stimuli using a button box. These tests may assess conditions like AMD as well as assess efficacy of gene therapies, in clinical and clinical trials use
Sweep VEP
Sweep VEP objectively assesses visual acuity. The method utilizes a black & white, low contrast checker board pattern onset method to stimulate a fixating patient. A Laplace transform and Fourier analysis is performed in automatically estimating visual acuity. Tests are available for normal, low, and very low vision patients and can be useful for those with unexplained, psychogenic, or non-organic vision loss.
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.