Mastering Automated Perimetry: Essential Tips and Tricks for Optometrists
As optometrists, mastering the art of automated perimetry is essential for accurate diagnosis and management of optic neuropathies. Automated perimetry, also known as visual field testing, provides valuable information about afferent dysfunction and disease progression. In this article, we will explore some essential tips and tricks to enhance your proficiency in this specialized field.
Familiarize Yourself with Testing Strategies:
Understanding various testing strategies is crucial for efficient and accurate perimetry. The evolution of automated perimetry techniques, such as the Full Threshold, SITA Fast, and SITA Faster algorithms, have revolutionized the field.
Stay updated with the latest advancements and their unique features to choose the most appropriate strategy for each patient. Familiarize yourself with the specific testing parameters and algorithms associated with each strategy to optimize test accuracy.
Humphrey Field Analyzer (HFA) test strategies have been developed over the years to improve the efficiency and reliability of automated perimetry.
- Full Threshold: The Full Threshold strategy was one of the early HFA algorithms. It tested the central 30 degrees of the visual field at intervals of 6 degrees, determining the threshold value for each point location through a “double crossing” method. While effective, this strategy had a long test duration of approximately 15 minutes per eye.
- SITA Fast: In the late 1990s, Bengtsson and Heijl developed the Swedish Interactive Threshold Algorithm (SITA), which introduced time-saving changes while maintaining reliability. The SITA Fast strategy incorporated several modifications to decrease test duration while limiting variability. It included tester-influenced variables like stimulus speed and estimations of thresholds based on test responses. This strategy reduced test time by half compared to the Full Threshold test.
- SITA Faster: Building on the success of SITA Fast, the SITA Faster strategy was created as an updated version in the 2010s. It further reduced test duration by implementing additional time shortcuts. Changes included testing the primary points only once instead of twice, discontinuing false-negative catch trials, relying on gaze tracking, and removing the delay after an unseen stimulus. SITA Faster decreased test time by an additional 30% compared to SITA Fast and 50% compared to the Full Threshold strategy.
These HFA test strategies aimed to balance test duration and accuracy, making visual field testing more efficient for patients while maintaining reliable results. By utilizing these strategies, optometrists can reduce test variability and improve patient comfort during the perimetry process.
It’s important for optometrists to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in HFA test strategies as they continue to evolve and offer new features to enhance automated perimetry.
Optimize Test Parameters:
Optimizing test parameters ensures reliable and consistent results. Adjusting test duration, stimulus intensity, and testing locations can impact both test sensitivity and patient comfort. Balancing between test duration and accuracy is vital, especially when utilizing time-saving strategies like SITA Fast or SITA Faster algorithms.
Experiment with different parameters to find the optimal settings for each patient, considering factors such as age, visual acuity, and disease severity.
Understand Kinetic and Static Perimetry:
Being well-versed in both kinetic and static perimetry is essential. Kinetic perimetry utilizes moving stimuli to determine threshold values, while static perimetry employs stationary stimuli. Understanding the differences, advantages, and limitations of each technique enables you to choose the most appropriate approach for specific clinical scenarios. Kinetic perimetry may be preferred in cases where there are suspected areas of visual field loss, while static perimetry is useful for comprehensive mapping of the visual field.
Utilize Virtual Reality Perimetry (VRP):
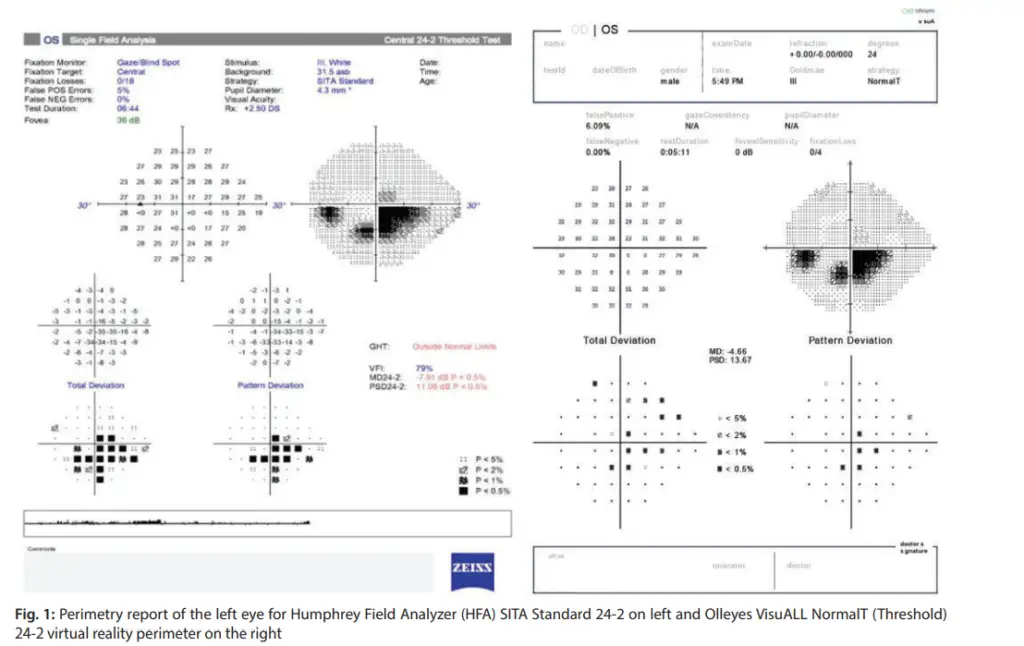
The emergence of Virtual Reality Perimetry (VRP) presents exciting opportunities for expanding the perimetry field. VRP offers portability, making it suitable for remote testing. It also provides flexibility in patient positioning, overcoming limitations in traditional perimetry setups. Stay updated with VRP developments and consider integrating this technology into your practice. Evaluate different VRP systems and understand their features, benefits, and limitations to determine their suitability for your patients.
Monitor Technological Advancements:
Keeping up with technological advancements is crucial for providing the best care. Stay informed about new devices, software updates, and validation studies to ensure you are utilizing the latest tools effectively. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of different devices will assist in making informed clinical decisions. Regularly attend conferences, workshops, and training sessions to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in automated perimetry.
Establish Patient Rapport and Compliance:
Patient cooperation and understanding play key roles in achieving accurate results. Establish a good rapport with patients, carefully explain the procedure, and address any concerns they may have. Encourage compliance by providing clear instructions and reiterating the importance of maintaining focus throughout the test. Educate patients about the significance of visual field testing in their overall eye health and the role it plays in their treatment and management plan.
Regularly Review and Update Normative Databases:
Normative databases provide a valuable reference for interpreting perimetry results. Regularly review and update your knowledge of normative databases to ensure accurate interpretation, considering age, race, and other relevant factors. Being familiar with normative data aids in early detection and tracking of visual field defects. Interpret results in the context of each patient’s individual characteristics and clinical history to make informed clinical decisions.
Combine Automated Perimetry with other Diagnostics:
Perimetry is just one piece of the diagnostic puzzle. Combine visual field testing with other diagnostic tools, such as optic coherence tomography (OCT) or fundus photography, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition. Integrating multiple diagnostic modalities enhances diagnostic accuracy and enables personalized treatment plans. Collaborate with other eye care professionals and specialists to create a multidisciplinary approach to patient care.
Also read-
Reading the Humphrey visual field test printout.
Conclusion:
Mastering automated perimetry is a crucial skill for any optometrist aiming to excel in the field of glaucoma and optic neuropathies. By understanding testing strategies, optimizing test parameters, staying up-to-date with technological advancements, and building rapport with patients, you can enhance the reliability and accuracy of your visual field assessments.
Combining perimetry with other diagnostic tools further strengthens your ability to diagnose and monitor patients effectively. Embrace the advancements in virtual reality perimetry and continue to refine your expertise in this ever-evolving field. By constantly seeking knowledge, staying current with technological advancements, and integrating multiple modalities, you can provide optimal care and improve patient outcomes.
For more details you can read this
Follow us in Facebook for Diagnosis challenge
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.