Multifocal for Astigmatism Fitting Guide: A Comprehensive Approach
Fitting multifocal contact lenses for patients with astigmatism can be a complex task, given the dual challenge of correcting both presbyopia and astigmatism. However, with the advancements in lens technology, such as Bausch + Lomb ULTRA® Multifocal for Astigmatism lenses, eye care professionals can now offer their patients a solution that delivers clear, stable vision at all distances. This article serves as a comprehensive guide for fitting these multifocal toric lenses, outlining key steps and considerations for success.
Air optix multifocal fitting guide
Acuvue multifocal fitting calculator
The Challenge of Astigmatism and Presbyopia
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea or lens of the eye has an irregular shape, causing light to focus unevenly on the retina, leading to blurred or distorted vision. Presbyopia, on the other hand, is the age-related loss of the eye’s ability to focus on nearby objects. For patients who experience both of these refractive errors, the fitting of contact lenses becomes more challenging, as the lenses must correct for both distance and near vision while also compensating for astigmatism.
Multifocal toric lenses, like Bausch + Lomb ULTRA® Multifocal for Astigmatism, are specifically designed to address these dual needs. By incorporating technologies that stabilize the lens and ensure a smooth transition between near, intermediate, and distance vision, these lenses offer patients the clarity and convenience they need in their daily lives.
Fitting multifocal lenses for astigmatism involves a systematic approach to ensure both distance and near vision correction.
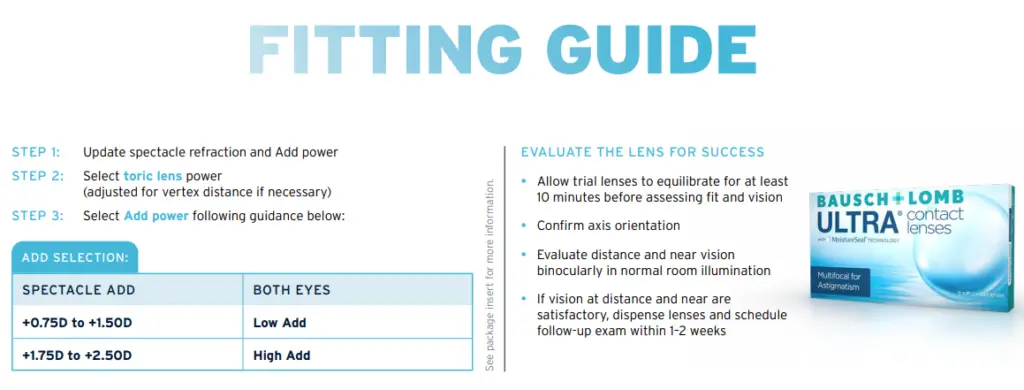
Step 1: Update Spectacle Refraction and Add Power
Before fitting the contact lenses, update the patient’s spectacle refraction. This includes determining both the sphere and cylinder powers as well as the add power for presbyopia. The add power typically falls within two ranges:
- Low Add: +0.75D to +1.50D
- High Add: +1.75D to +2.50D
Step 2: Select the Toric Lens Power
Select the toric lens power based on the patient’s refractive error. Adjust for vertex distance if necessary. For accurate lens fitting, always refer to the spectacle refraction to determine the spherical and cylinder powers, and align the axis according to the refractive prescription.
Step 3: Select the Add Power
Once the toric lens power is chosen, select the appropriate Add Power for both eyes:
- If the spectacle Add is between +0.75D and +1.50D, it is a Low Add.
- If the spectacle Add is between +1.75D and +2.50D, it is a High Add.
Step 4: Evaluate the Lens for Success
After inserting the trial lenses, follow these steps to ensure the lens fits properly and provides clear vision:
- Equilibration: Allow the trial lenses to settle for at least 10 minutes before evaluating the fit.
- Axis Orientation: Confirm that the toric lens aligns properly with the prescribed axis.
- Visual Assessment: Evaluate the patient’s binocular vision in normal room illumination at both distance and near.
If the patient’s distance and near vision are satisfactory, dispense the lenses and schedule a follow-up visit within 1–2 weeks.
Near Vision Refinement:
For Patients Wearing Two Low Adds:
- Initial Lens: Both the dominant and non-dominant eyes are fitted with Low Add lenses.
- Refinement 1: If near vision isn’t satisfactory, change the non-dominant eye to a High Add.
- Refinement 2: If the vision is still unsatisfactory, make small adjustments by adding +0.25D to the non-dominant eye wearing a High Add lens, using hand-held lenses. Continue evaluating vision binocularly in normal room lighting, adjusting the power until the patient achieves satisfactory vision.
For Patients Wearing Two High Adds:
- Initial Lens: Both eyes are fitted with High Add lenses.
- Refinement 1: Add +0.25D to the non-dominant eye.
- Refinement 2: If vision is still unsatisfactory, make small changes by adding +0.25D at a time to the non-dominant eye using hand-held lenses, evaluating the vision binocularly in normal lighting until satisfactory vision is achieved.
Distance Vision Refinement:
For Patients Wearing Two Low Adds:
- Initial Lens: Fit both the dominant and non-dominant eyes with Low Add lenses.
- Refinement 1: If distance vision is unsatisfactory, switch the dominant eye to a Bausch + Lomb ULTRA® Multifocal for Astigmatism lens.
- Refinement 2: If distance vision is still not clear, make small changes by reducing -0.25D at a time from the dominant eye using hand-held lenses. Continue evaluating vision binocularly in normal room lighting and adjusting power until the patient has satisfactory distance vision.
For Patients Wearing Two High Adds:
Refinement 2: If vision is still unsatisfactory, make small changes by reducing -0.25D at a time to the dominant eye. Evaluate binocular vision in normal lighting and adjust the lens power until vision is satisfactory..
Initial Lens: Fit both the dominant and non-dominant eyes with High Add lenses.
Refinement 1: Change the dominant eye to a Low Add lens.

Hope you found this fitting guide helpful.
Join our Daily eye care challenge in Facebook
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


You must be logged in to post a comment.