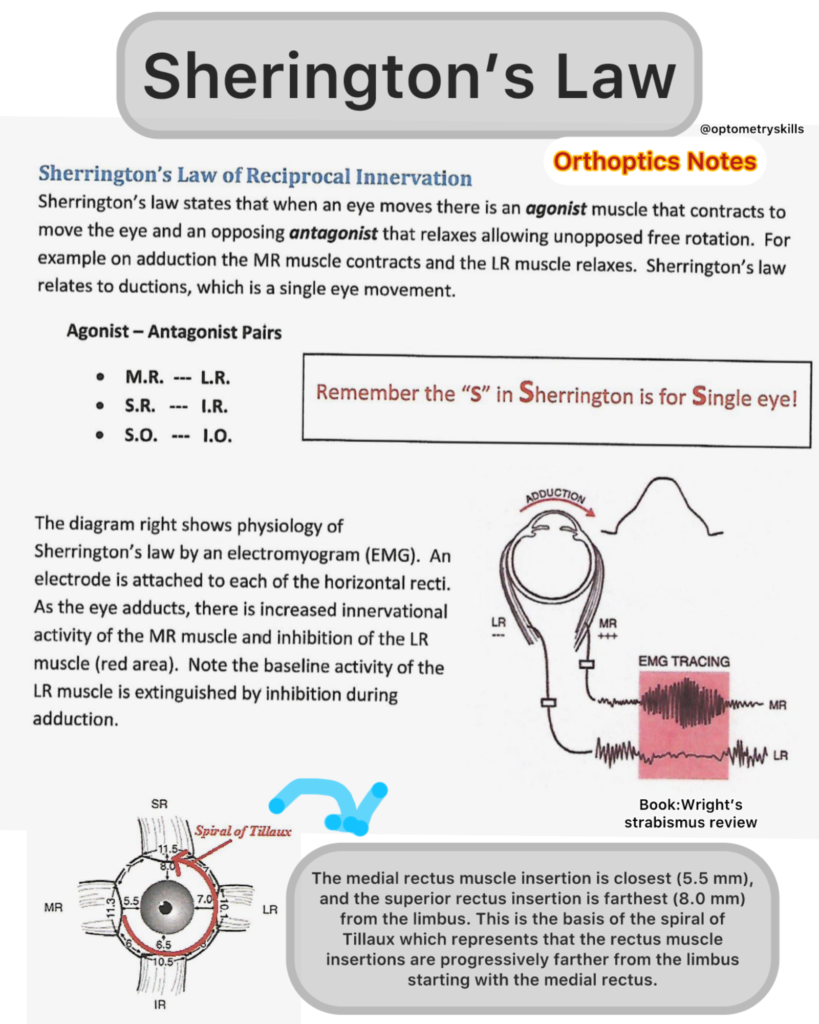
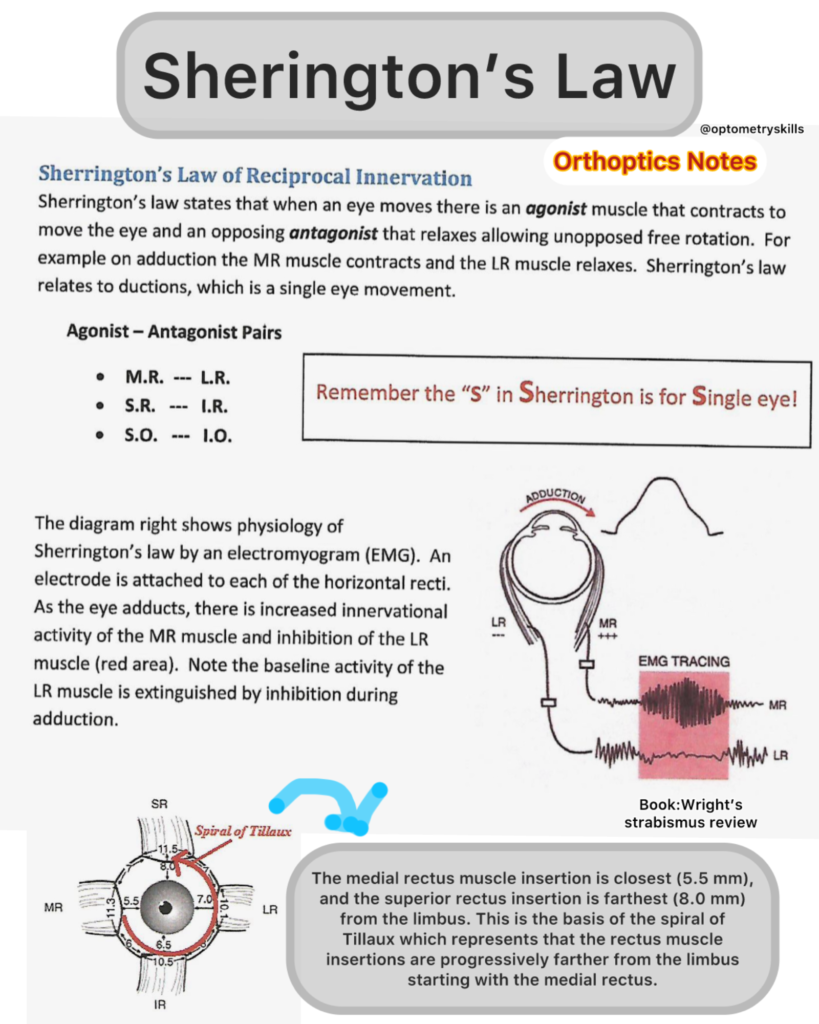
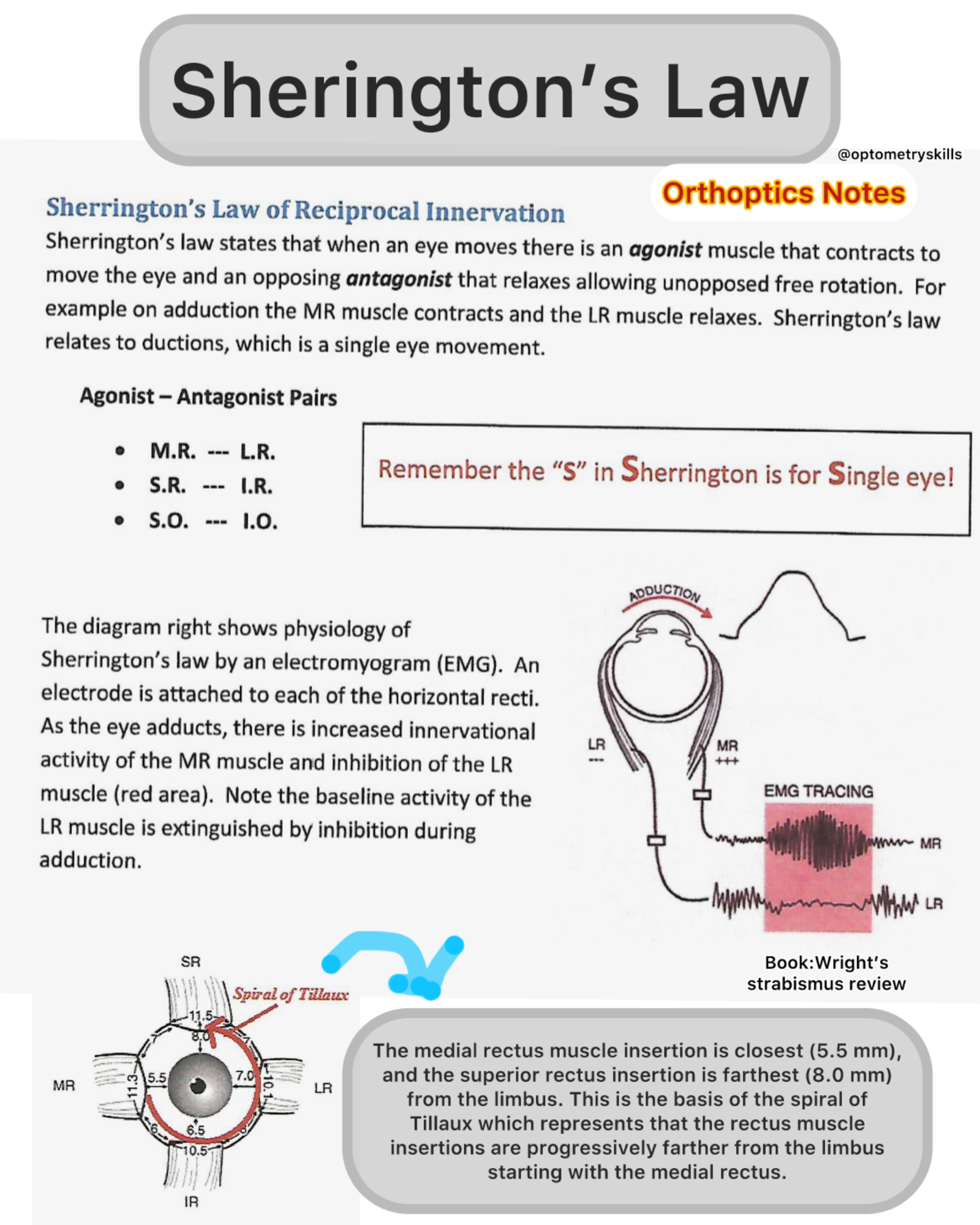
What is Sherrington’s Law of Reciprocal Innervation ?
Sherrington’s law states that when an eye moves there is an agonist muscle that contracts to
move the eye and an opposing antagonist that relaxes allowing unopposed free rotation. For
example on adduction the MR muscle contracts and the LR muscle relaxes. Sherrington’s law
relates to ductions, which is a single eye movement.
Agonist – Antagonist Pairs
- M.R. — L.R.
- S.R. — I.R.
- S.O. — 1.0.
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.