image credit
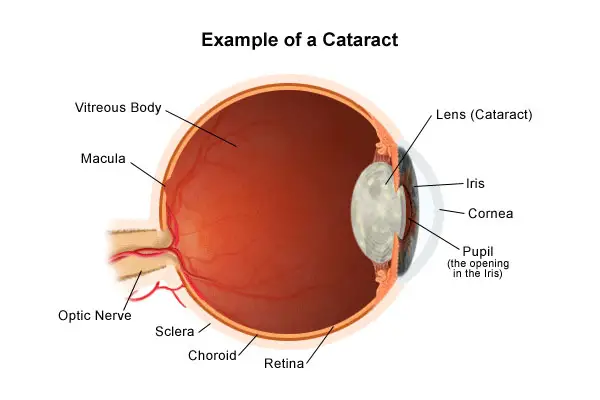
Cataract is a clouding of the lens or any opacity within the lens which leads to a decrease in vision.
Also read what is therapeutic optometry?
cataract definition
Normal crystalline lens is a transparent structure. Any opacity in the lens or its capsule is called a cataract.

Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of cataracts include:
- Clouded, blurred or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing “halos” around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye
How do you classify cataracts?
Etiological classification of cataract:
I. Congenital and developmental cataract
II. Acquired cataract
- Senile cataract
- Traumatic cataract
- Complicated cataract
- Metabolic cataract
- Electric cataract
- Radiational cataract
- Toxic cataract, e.g.,
a. Corticosteroid-induced cataract
b. Miotics-induced cataract
c. Copper-induced and iron-induced cataracts
(in chalcosis and siderosis respectively). - Cataract associated with skin diseases
(dermatogenic cataract). - Cataract associated with osseous diseases.
- Cataract associated with miscellaneous syndromes e.g.,
- Dystrophic myotonica
- Down’s syndrome.
The treatment of cataracts is :
- Glasses
- Better lighting
- Surgery
a. Phacoemulsification
b. ECCE
c. ICCE (not performed now)
Sometimes a cataract should be removed even if it doesn’t cause major problems with vision, if it is preventing the treatment of another eye problem, such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy or retinal
Discover more from An Eye Care Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

You must be logged in to post a comment.